Here we will discover the secrets of creating compelling data stories with Power BI Waterfall Charts, ribbon charts Power BI and drill-down feature. In the grand orchestra of data visualization, the Power BI waterfall chart plays a lead role.
Table of Contents
waterfall chart power bi
You can consider yourself embarking on a journey from a starting point. And as we expect, you are navigating through ups and downs. This is the essence of a Power BI waterfall chart.
Each bar in the chart expresses a part of your story that will provide insight into how initial numbers become final results. It’s like a tale of numbers.
Summary of waterfall chart in power bi
As a result, whether you are plotting Power BI waterfall chart or trying to reproduce an Excel waterfall chart, you are creating combo charts power bi it’s all about narrating your story.
Understanding Waterfall Charts and ribbon charts Power BI
Waterfall Charts in Power BI visually represent sequential impact on data. This is making them essential for financial analysis and inventory management. They begin with a starting value. It is followed by increments (positive values) and decrements (negative values). Hence, these are culminating in a final result.
This makes them particularly useful for visualizing financial statements, project budgets or any scenario.
But why stop at a Power BI waterfall chart?
What Are Power BI Waterfall Charts?
For those moments when your story needs a dynamic duo, the combo chart Power BI steps into the spotlight. It combines the strength of a column chart (ribbon chart Power BI) with the precision of a line chart. This is allowing you to track two related data sets simultaneously.
But what if your story is more about leads or stages, like the journey of a sales prospect? Power BI funnel chart (ribbon chart Power BI) guiding your audience through a process from the widest point of initial interest down to the narrow end of final action.
-
Key Takeaways
- Before you start with any customization, you should ensure your data is well-prepared. An organized dataset is the backbone of an effective Power BI waterfall chart.
- The Power BI change color of bar chart (ribbon chart Power BI) feature (drill-down feature) is not just about aesthetics. It is about improving readability and comprehension. Color coding different elements of your chart helps convey your data’s story more effectively.
- Data labels and tooltips are essential for providing context. They make your Power BI waterfall chart or Power BI funnel chart more informative.
- Adding breakdowns or subtotals can significantly enhance your chart’s analytical value.
- The formatting of axes, titles and overall layout plays a huge role in how your data visuals. Clear titles and axes are key to a successful chart.
- Incorporating drill-down features into your chart, enhances user engagement.
Why Waterfall Charts Matter in Project Management
The beauty of Power BI waterfall charts lies in their ability to break down complex project financials, performance metrics or any sequential data set into understandable segments. This visualization not only clarifies the impact of individual components on the overall project. But also aids in pinpointing areas requiring attention.
In project management, every decision counts. And understanding the story behind your data can make the difference between success and setback. Power BI waterfall charts offer a clear visual narrative of where resources are allocated.
Creating a Waterfall Chart in Power BI
To craft a Waterfall Chart in Power BI, you should begin by ensuring your dataset is structured to support this visualization type.
- You should focus on the key figures you wish to analyze.
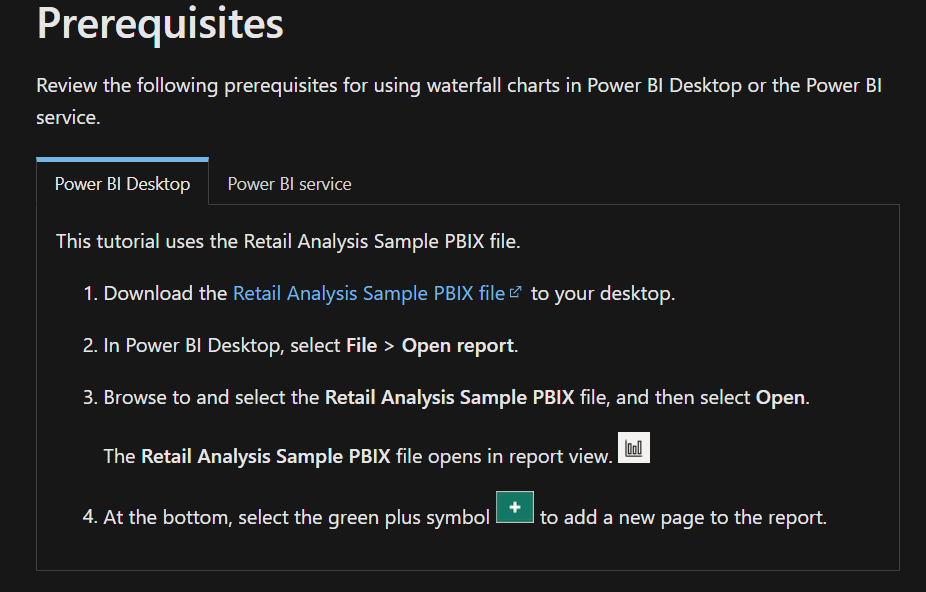
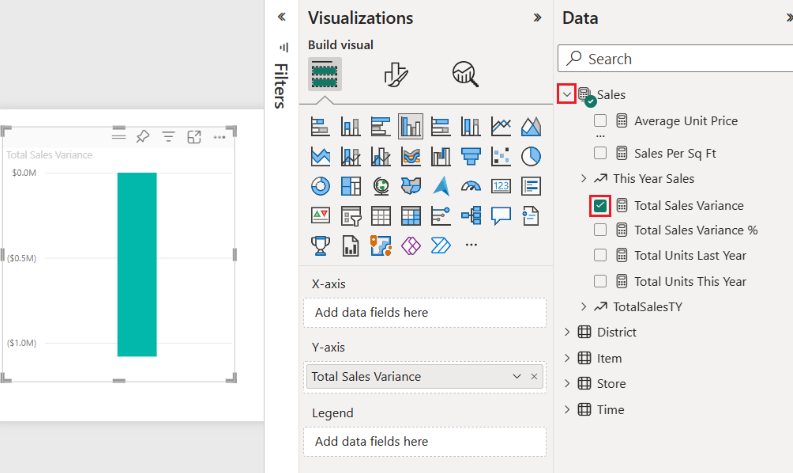
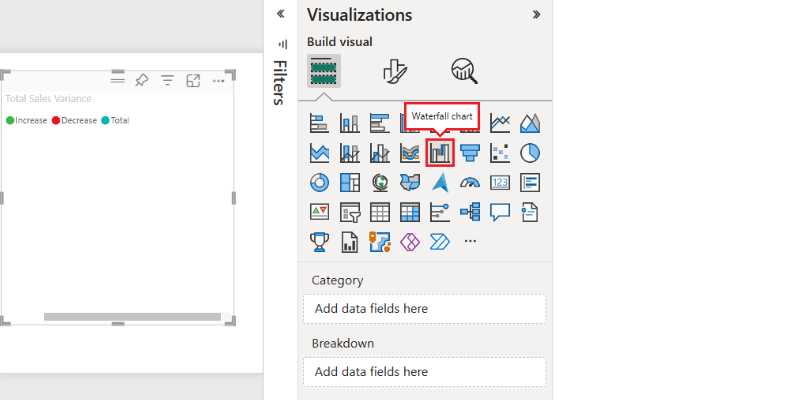
- then, choose the Waterfall Chart visualization in the Visualizations pane.
- You should assign data fields and drag your category field (e.g., time periods, transaction types) to the Axis area and your value field.
- You can further dissect your data by adding a breakdown category.
Customizing Your Waterfall Chart in Power BI: Step by Step!
Customization can dramatically enhance the effectiveness of your Waterfall Chart.
- You can use distinct colors to differentiate between increases, decreases and totals.
- Then, you can enable data labels for immediate value recognition and consider formatting them for clarity.
- You can customize tool tips to provide additional context when users hover over data points.
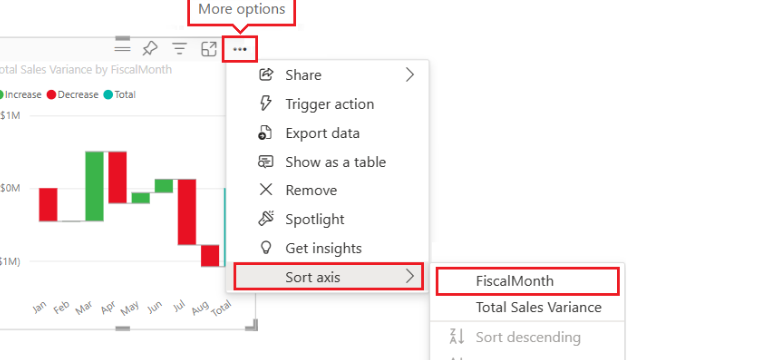
- Also, you need to adjust the titles, labels and scale to fit your data narrative.
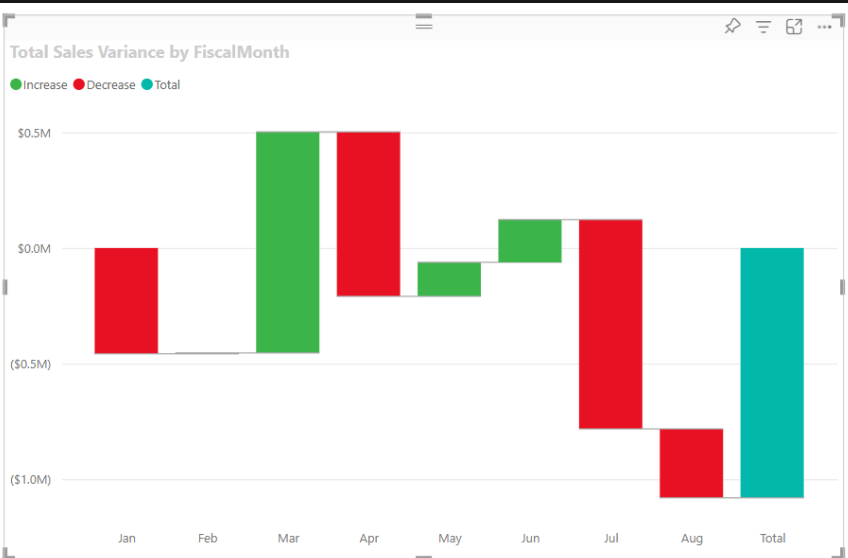
Customizing your Power BI waterfall chart is a step to ensure for visualization. Because it accurately represents your data. But it also engages and informs your audience effectively. The flexibility of Power BI allows you to tailor your waterfall charts to meet specific requirements.
Interpreting Waterfall Charts in Power BI
The initial bar typically represents the starting value. And it is followed by subsequent bars indicating increases or decreases. This layout helps identify key contributors to financial outcomes or other metrics.
Advanced Tips and Tricks
Drill-Downs
For example, you are showing off your Power BI waterfall chart that depicts your company’s quarterly earnings. It looks great, but then someone asks, “What exactly contributed to that surprising spike in March?” A click, and voila, you reveal the layers beneath. Maybe it was an unexpectedly successful product launch or a major contract acquisition. This feature doesn’t just show data. But it tells the story behind the numbers.
Custom Calculations
AX (Data Analysis Expressions) is your wand for crafting custom calculations. For example, let’s say your chart tracks monthly revenue. But you want to factor in projected increases from a new marketing strategy. With DAX, you can add these forecasted figures directly into your chart.
Dynamic Segmentation
This is where slicers and filters come into play. And they are transforming your chart. It adjusts to show exactly what your audience wants to see.
You are presenting annual sales data. But then someone is curious about how a specific region performed in Q2. With a few clicks, your chart reshapes to focus on that particular interest.
Bringing It All Together
As you walk them through the figures, you can use drill-downs to reveal the story behind a surprising dip in April. You can introduce a DAX calculation that predicts recovery thanks to a new client onboarding in July.
To cap it off, you can demonstrate dynamic segmentation. And you are isolating the impact of the North American market.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Don’t Let Complexity Cloud Your Vision
You are trying to explain how your company’s revenue has changed over the quarter. And instead of focusing on the main factors like new sales, returns and net changes, you toss in every single sale and return transaction. Suddenly, your audience needs a magnifying glass. So, you can highlight the stars of the show and leave the extras for the director’s cut.
Data Alignment Matters
For example let us imagine you are presenting a Power BI waterfall chart to highlight changes in monthly revenue. If April’s numbers accidentally get tagged with March’s label, your stakeholders will be scratching their heads. That’s why it’s really important to make sure all your data is in order and properly labeled!
Conclusion
When you start playing around with drill-down capabilities, adding a custom calculations with DAX and use some dynamic segmentation, you are not just making charts, you are crafting narratives.

A dedicated Career Coach, Agile Trainer and certified Senior Portfolio and Project Management Professional and writer holding a bachelor’s degree in Structural Engineering and over 20 years of professional experience in Professional Development / Career Coaching, Portfolio/Program/Project Management, Construction Management, and Business Development. She is the Content Manager of ProjectCubicle.